| d = distance (usually in metres) | 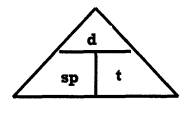 |
| sp = speed (usually in m/s) | |
| t = time (usually in seconds) |
MOVE
IT!
Use these questions to help you revise. Move
the mouse over the hidden text in the
answer box to see the example answers
| d = distance (usually in metres) |  |
| sp = speed (usually in m/s) | |
| t = time (usually in seconds) |
|
QUESTIONS |
ANSWER BOX |
|
|
1. |
If a car travels 1000 metres in 50
seconds, what is its average speed? |
20
m/s
|
|
2. |
A sprinter covers 100 m at an average
speed of 10 m/s How long did she take? |
10
seconds.
|
|
3. |
A car goes from London to Leeds, a
distance of 200 miles, in 4 hours. What is its average speed? |
50
miles per hour.
|
|
4. |
A bicycle travels at 5 m/s for 5
minutes. How far does it travel? |
60
x 5 = 300 seconds
|
|
|
|
300
seconds x 5 m/s 1500 metres. |
|
5. |
If a loaded lorry and a small car were
travelling along together at the same speed, when suddenly they were
forced to stop, which vehicle do you think would stop the fastest? |
The
small car
|
|
6. |
Explain why you have given the answer
above. |
The
small car is lighter and has less momentum than the heavy lorry |
|
7. |
When a vehicle brakes, movement energy
is changed into _ energy in the brakes. |
Heat.
|
|
8. |
What do we call the grip between the
tyres of a vehicle and the road? |
Friction.
|
|
9. |
Some lorries have large pieces of
plastic on their roofs, to help reduce fuel costs |
|
|
|
|
a)
Streamlining, |
|
|
|
b)
The vehicle cuts through the air more easily, reducing fnction and
therefore reducing the energy needed to keep the vehicle moving. |
|
9. |
Katy is riding downhill on her bike.
She goes faster but the wind becomes greater as she goes faster |
|
|
|
a) What do we call gaining speed? |
|
|
|
b) What do we call the wind stopping
her? |
|
|
|
c) What can she do to make herself go
even faster |
c)
Crouch down (change her shape -
streamlining), pedal faster. |