| Questions | Answers | ||||||||||
|
1.
F/H |
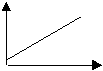
Describe
the motion shown by the following graphs:
|
|
(a)
stopped (b) steady
speed |
||||||||
|
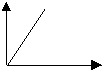
2.
F/H |
Sketch a
distance / time graph for something moving with a greater speed than (b)
above |
|
|||||||||
|
3.
F/H |
What is
the formula that connects speed, time and distance? |
|
speed =
distance / time |
||||||||
|
4.
F/H |
If a car
goes 200m in 10 seconds - what is it's speed? |
|
20m/s |
||||||||
|
5.
F/H |
What is
the difference between velocity and speed? |
|
The
velocity of an object is its speed in a given direction. |
||||||||
|
6.
F/H |
Sketch the
shape of a velocity / time graph for an object: (a) with
constant velocity |
|
|
||||||||
|
|
(b)
with constant acceleration |
|
|
||||||||
|
7.
F/H |
Describe
the difference between in the motion between these two graphs:
|
|
(a)
is accelerating less than (b) OR
(b) has greater acceleration |
||||||||
|
8.
F/H |
(a) What
is the formula that connects acceleration, velocity and time?
(b) If an object
speeds up from 20m/s to 100m/s in 4s, what is it's acceleration? |
|
(a) a =
change in velocity / time taken (b) a = (100-20)/4 =
20m/s/s |
||||||||
|
9.
H |
What
does the gradient of distance time graph tell us? |
|
It's speed |
||||||||
|
10.
H |
(a) What
does the gradient of a velocity/time graph tell us?
(b) what does the area under the graph tell us? |
|
(a)
acceleration (b) distance |
||||||||
|
11.
H |
Sketch a velocity time graph for the following data: an object that goes from 2m/s to 10m/s in 4s use the graph to calculate: (a) the acceleration of the object (b)
the distance traveled by the object. |
|
Gradient = 4m/s/s = acceleration Area = 24m
= distance |
||||||||
|
12.
F/H |
When an
object is at rest on a surface - what can you say about the forces on
it? |
|
The cancel
each other out (balance) |
||||||||
|
13.
F/H |
For the
above: What force acts downwards on the surface? |
|
the weight |
||||||||
|
14.
F/H |
For the
above: What force acts upwards? |
|
A reaction
force (the surface pushing upwards on the object) |
||||||||
|
15.
F/H |
For the
above: What can you say about the size of the two forces |
|
They are
the same |
||||||||
|
16.
F/H |
When two
bodies interact (push on each other) the forces they exert on each other
are ______ and _________. |
|
equal,
opposite |
||||||||
|
17.
F/H |
_________
forces will have no effect on the movement of an object |
|
balanced |
||||||||
|
18.
F/H |
When an
object is not moving what effect will a balanced force have on the
object? |
|
it will
remain stationary |
||||||||
|
19.
F/H |
When an
object is moving - what effect will a balanced force have on the object? |
|
it will
continue to move at the same speed and in the same direction |
||||||||
|
20.
F/H |
__________
forces are forces on an object that do not cancel out |
|
unbalanced |
||||||||
|
21.
F/H |
How an
unbalanced force affect an object can depend on two things - what are they? |
|
the
direction and the size of the unbalanced force: |
||||||||
|
22.
F/H |
Describe
the motion of a stationary object if an unbalanced force acts on it |
|
It will
start to move in the
direction of the force. It
will speed up in the direction of the unbalanced force. |
||||||||
|
23.
F/H |
Describe
the motion of a moving object if an unbalanced force acts on it. |
|
An object
moving in the direction of the force will speed up. An object moving in the opposite direction to the force will slow
down |
||||||||
|
24.
F/H |
How does
the size of the unbalanced force affect the way the object will speed up
or slow down? |
|
the
greater the size of the unbalanced force, the faster the object will
speed up or slow down |
||||||||
|
25.
F/H |
How will
the mass of the object affect the way it speeds up or slows down? |
|
The bigger
the mass of an object, the greater the force needed to give the object a
particular acceleration |
||||||||
|
26.
H |
What is a
newton? |
|
The unit
of force. It is the force needed to give a
mass of one kilogram an acceleration
of one metre per second
squared. |
||||||||
|
27.
H |
How are
force mass and acceleration related? |
|
F
= m x a |
||||||||
|
28.
F/H |
A force of
_______ acts when an object moves through air or water |
|
friction |
||||||||
|
29.
F/H |
A force of
_________ acts when solid surfaces slide (or tend to slide) across each
other |
|
friction |
||||||||
|
30.
F/H |
The
direction of friction is always ________ to the direction in which the
object is moving |
|
opposite |
||||||||
|
31.
F/H |
The
friction between solid surfaces is used in ________ which slow down and
stop moving vehicles |
|
brakes |
||||||||
|
32.
F/H 33.
F/H |
The
greater the speed of a vehicle: the
________ the braking force needed to stop it in a certain distance the
_______ the distance needed to stop it with a certain braking force |
|
greater greater |
||||||||
|
34.
F/H |
If too
great a braking force is applied, friction between a vehicle's tyres and
the road surface may not be great enough to prevent _________ |
|
skidding |
||||||||
|
35.
F/H |
What 2
things does the stopping distance of a vehicle depends on? |
|
(1) the
distance the vehicle travels during the driver's reaction time (2) the
distance the vehicle travels under the braking force |
||||||||
|
36.
F/H |
What does
overall stopping distance depend upon? (4 things) |
|
speed of
vehicle, driver's reactions (due to tiredness, drugs, alcohol), if there
are adverse weather conditions (wet/icy roads, poor visibility), if the
vehicle is poorly maintained (e.g. worn brakes/tyres). |
||||||||
|
37.
F/H |
When an
object is moving faster through a fluid - how does this affect the force
of friction on it? |
|
the force
of friction increases if the objects is moving faster |
||||||||
|
38.
F/H |
Explain
why objects have "terminal velocity" when they fall |
|
When a
body falls: initially it accelerates due to the force of gravity frictional
forces increase until they balance the gravitational forces; the
resultant force eventually reaches zero and the body fall at its
terminal velocity. |
||||||||
|
39.
F/H |
If an
object has steady speed - what can we say about the frictional forces
and the driving force? |
|
they
balance out |